Applicable to Tabular Compatibility Level:
SQL 2012 SP1 / SQL 2014 (1103) | SQL 2016 (1200) | SQL 2017 (1400)
Unlike Multidimensional projects, Tabular projects in SQL 2012 do not support translations. This feature gap makes Tabular models less user-friendly when the users are international since the field list in Excel PivotTables and Power View is not in their native language.
Another common scenario where this BI Developer Extensions feature helps is the following. Imagine you are a developer building a Tabular model for users who speak Hebrew natively. It may be easier to code the model with English table and column names so that your DAX would be more readable. But then you want to show your model to users with Hebrew table and column names. This BI Developer Extensions feature would let you code in English but display to users in their native language.
Warning: While translations of metadata work in Tabular models, they are not officially supported by Microsoft. If you encounter a bug in how Tabular handles translations and open a support case, Microsoft may not provide support.
BI Developer Extensions provides a UI for editing translations on metadata (not on data). The following objects can be translated:
- Database caption
- Cube caption
- Perspective caption
- Table caption and description
- Column caption, display folder, and description
- Measure caption, display folder, and description
- Hierarchy caption, display folder, and description
- Level caption
- Action caption and description
Note: Only metadata is translated (i.e. column names) not the data (i.e. values in the rows in tables) since Tabular models do not support translating data like Multidimensional models do.
To launch this feature, right click on the .bim file and choose Tabular Translations Editor…
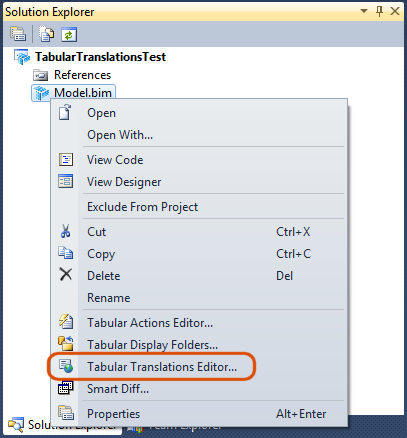
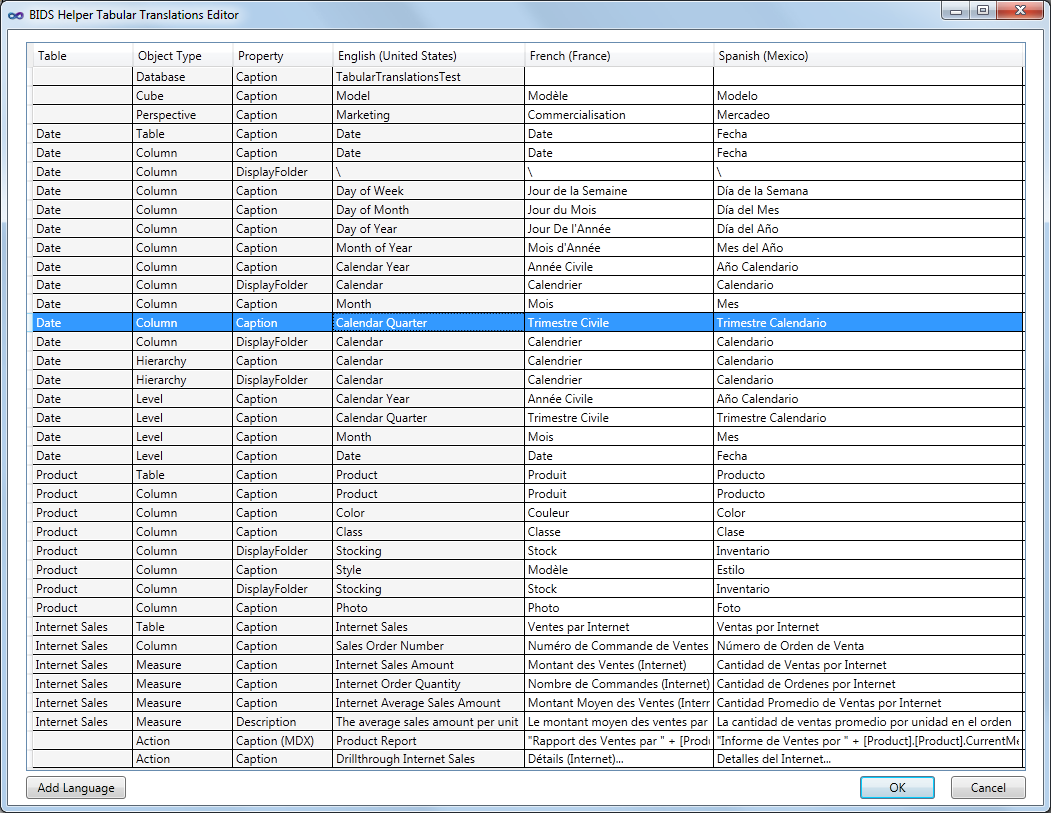
That launches the UI for editing translations. The first thing to do is to click the Add Language button to add your first translation language:
This screen contains the following columns:
- Table - A read-only column showing the name of the table containing the Column, Measure, Hierarchy, or Level. For other objects like Database, Cube, Perspective, and Action the column will be blank.
- Object Type - A read-only column identifying the type of object which you’re translating.
- Property - A read-only column showing whether that row lets you edit translations for the Caption, DisplayFolder, or Description property.
- Note that only properties which have a value in the default language of the model will show up. For example, if your model is in English and you have a column called Color and that column has a display folder filled in (via the Tabular Display Folders feature) but has no description, this Translations dialog will show the DisplayFolder row but not the description row. These properties will appear in order. The first row for an object will always be the Caption. Then the DisplayFolder or Description row will be displayed if there is a value in the default language.
- Note that for rows where Object Type is Action, the Property column can say either “Caption” or “Caption (MDX)”. This indicates whether an MDX expression is expected or a literal string. See the screenshot below for an example of this.
- Default Language - A read-only column showing the value of the Property for the default language for the model. In the screenshots, “English (United States)” is the default language. For more information about languages in Tabular models, see this blog post by Cathy Dumas.
- Translation Languages - The subsequent columns are all editable. One column appears per translation language which has been added.
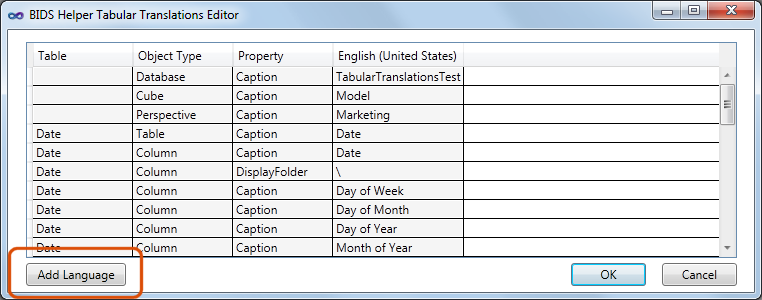
To remove a translation language completely, you can right click on the column header for a language:
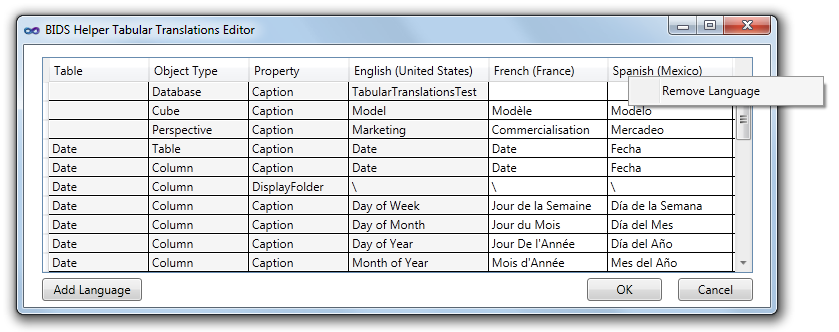
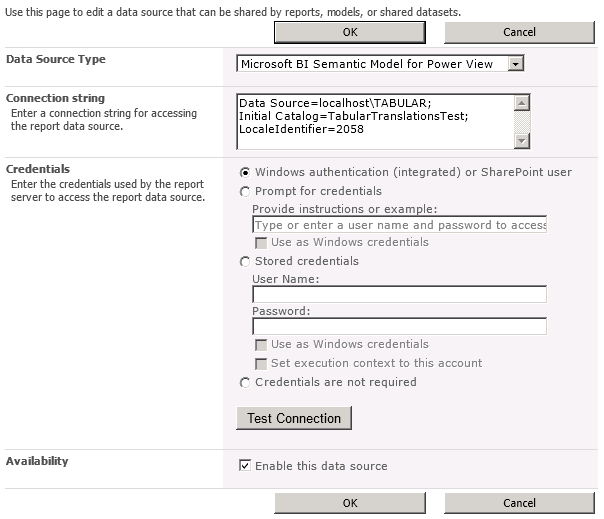
If you mouse over a column showing a language name, a tooltip will appear telling you the LCID for that language. You can use this value as the LocaleIdentifier connection string property, as will be shown below in the RSDS example:
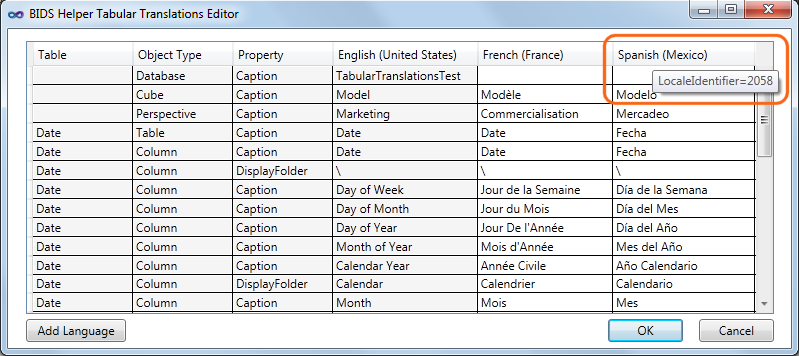
Once you have filled in translations, the dialog will look something like the following:
Excel PivotTables
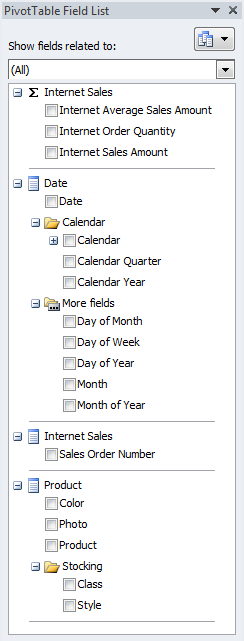
Once translated, if a user with the right language settings on their computer browses your Tabular model in Excel, the field list will display in their native language:
| English | Spanish |
|---|---|
 |
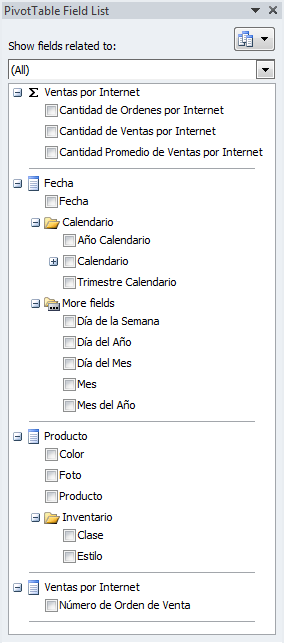 |
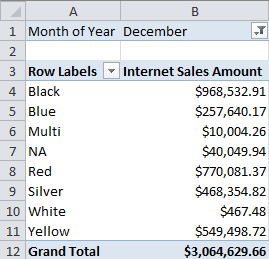
When building a PivotTable, notice that the field names retain the translations, but the data continues to show in the language of the data (in this case English all the time):
| English | Spanish |
|---|---|
 |
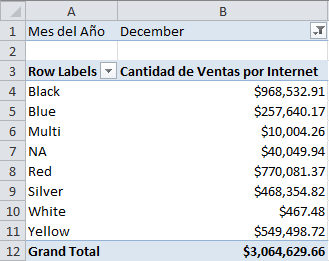 |
Power View Reports
Currently Power View (from SQL 2012 RTM version) always passes in LocaleIdentifier=127 to Analysis Services which causes the field list to display in the default language. In order to have Power View show a field list in a translated language, create an RSDS file by going to the document library, opening the Documents tab, dropping down the New Document menu, and choosing Report Data Source. (If this content type is not in the dropdown, then get your SharePoint administrator to add that content type to the document library.)
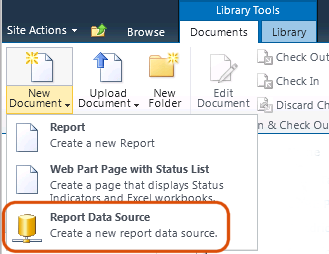
Then setup the RSDS and include the LocaleIdentifier connection string parameter. (Note, as shown above, mousing over the column header showing the translation language name will show you a tooltip with the proper LocaleIdentifier number.)
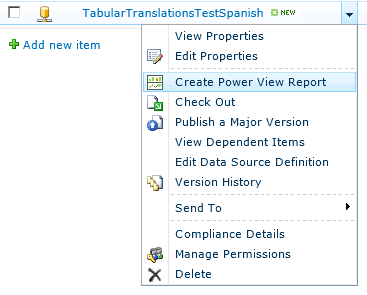
To create a new Power View report, pull down the context menu on the RSDS file and choose Create Power View Report:
Power View will then display the translated field list:
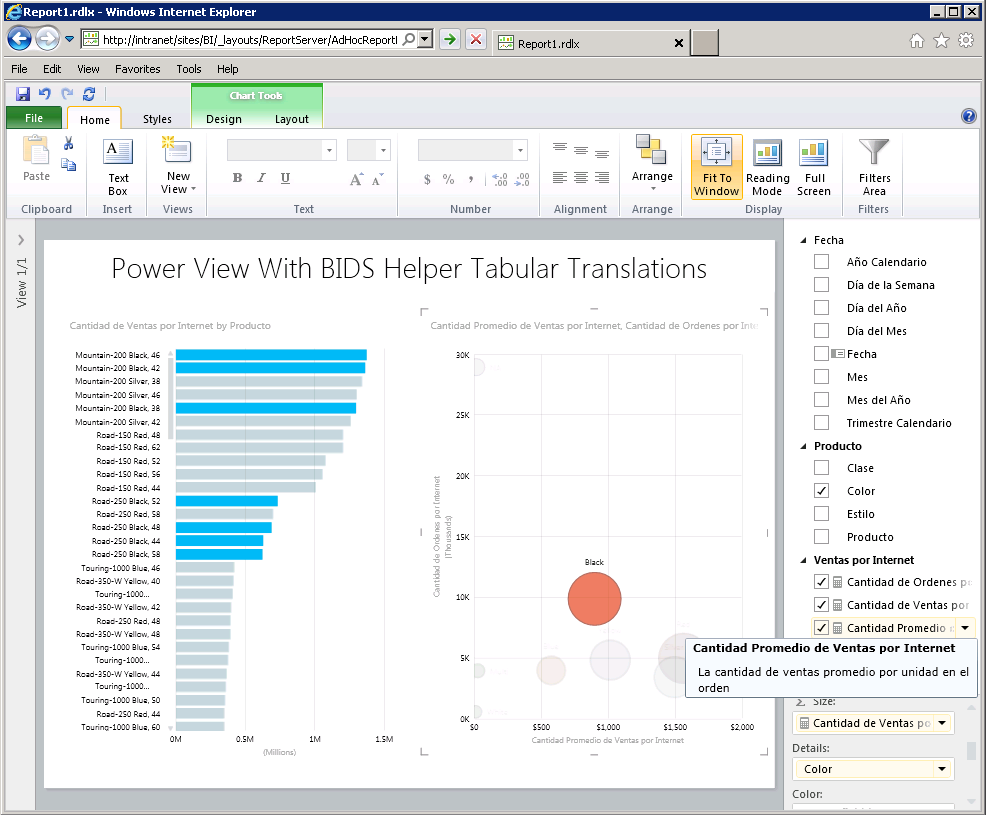
The Power View ribbon itself has been properly internationalized by Microsoft. If you install the Language Pack for the languages of your choice and install them, then the SharePoint user menu will let you change languages:
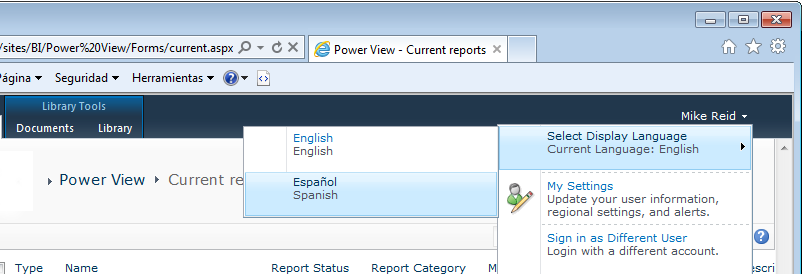
Once the SharePoint display language is changed, the Power View ribbon should display in that display language the next time you launch it:
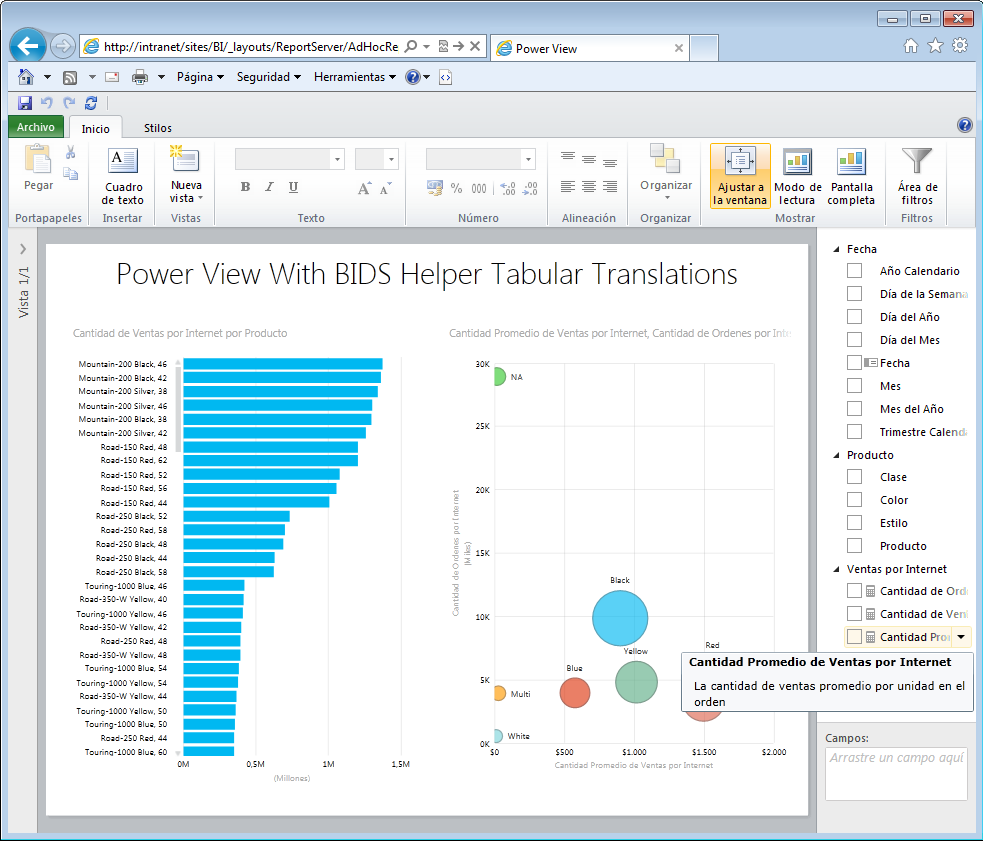
Best Practices:
- If you decide to translate one of the properties of an object, make sure to translate all of the properties of an object. For example, if you translate the caption of the ProductSubcategory column but don’t translate the description of that column, the description for that column will appear blank when viewed in that language. Note, if you translate the display folder or description property but do not translate the caption property on a particular object, BI Developer Extensions will use fill in the caption with the default language’s caption in order to prevent a blank caption for that language.
Limitations:
-
Note that some changes like reordering levels or setting format strings will wipe out the translations. BI Developer Extensions backs up the display folders in an annotation on the database. That way, the Tabular Pre-Build feature can prompt you to fix this setting.
-
Translations are not supported on Tabular KPIs currently due to a bug in Analysis Services.
After changing translations, BI Developer Extensions may prompt you for the credentials to a data source which is using stored credentials if you have not already entered those credentials during this SSDT editing session. This prompt ensures that data source credentials in the workspace database do not get wiped out as translations are applied.